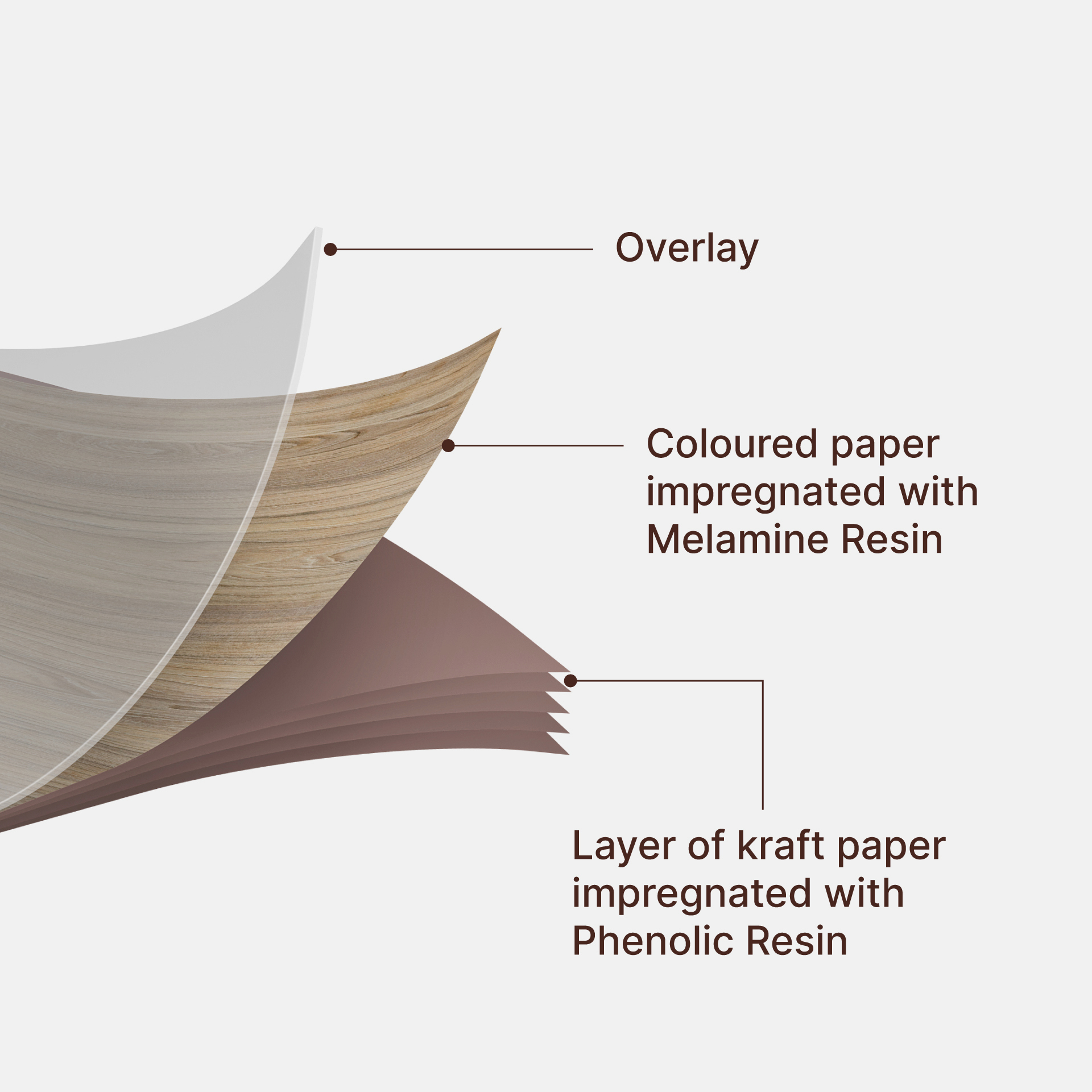
High Pressure Laminate (HPL)
High Pressure Laminates are a durable, versatile surfacing material. They’re typically made from layers of kraft paper impregnated with phenolic resin, topped with a decorative layer and a protective overlay. The entire stack is bonded under high heat and pressure to create a hard-wearing, low-maintenance surface. Known for their strength and resilience, HPLs are commonly used for countertops, cabinets, wall panels, and furniture. HPLs also require minimal maintenance and can withstand heavy wear and tear, which makes them ideal for high-traffic areas. In terms of sustainability, HPL manufacturers have adopted eco-friendly practices, such as using FSC-certified wood and recycled paper content in their laminates, reducing their reliance on virgin materials. This durability and reduced need for replacement make HPL an increasingly sustainable choice for interiors that combine longevity with aesthetic appeal.
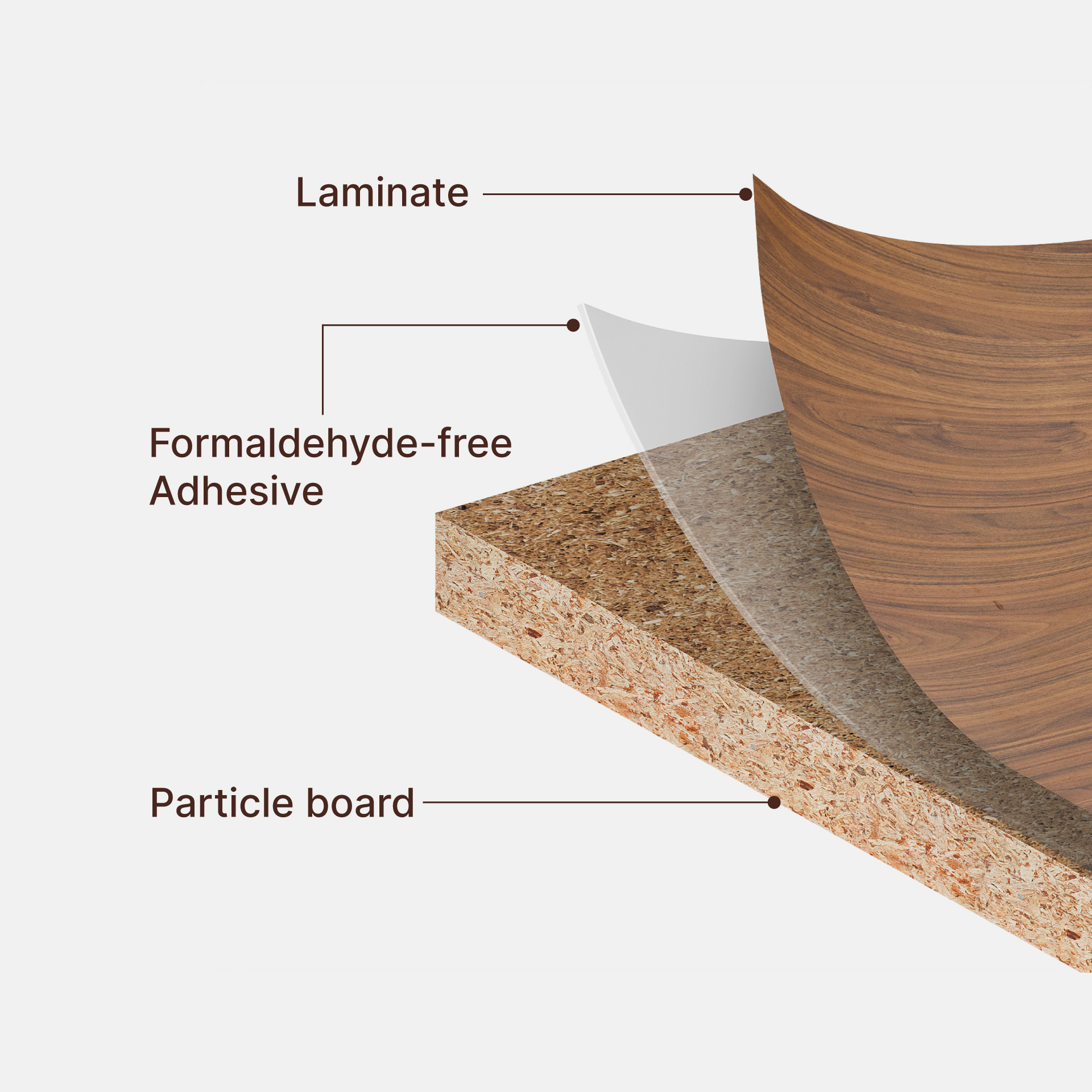
Zero Carb
Pre Laminated Board
Zero-Carb Pre-laminated Boards are engineered panels made without added formaldehyde or volatile organic compounds (VOCs), making them a healthier, eco-friendly alternative to traditional particleboards or MDF. These boards are typically made with sustainable, low-emission materials, and the term "zero-carb" indicates compliance with CARB (California Air Resources Board) standards, which regulate formaldehyde emissions.
In terms of sustainability, these boards are often manufactured from recycled wood fibers or responsibly sourced timber, ensuring minimal environmental impact. Their pre-laminated surfaces come in various designs and finishes, reducing the need for additional laminates or coatings that might add to waste and emissions. Additionally, zero-carb boards have high durability and resistance to moisture and wear, which extends their lifespan and reduces the frequency of replacements. This longevity, combined with low emissions and sustainable sourcing, makes zero-carb pre-laminated boards an ideal choice for environmentally conscious interior applications.
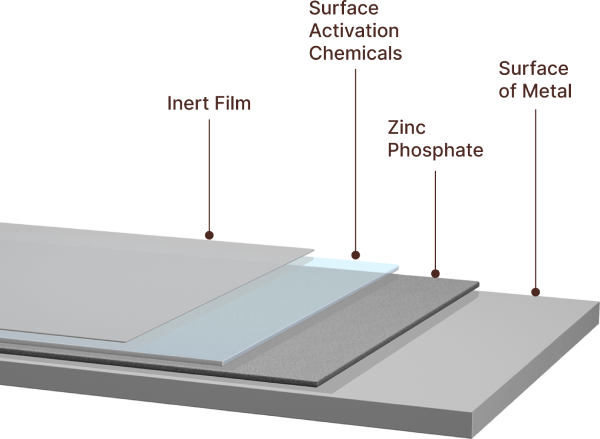
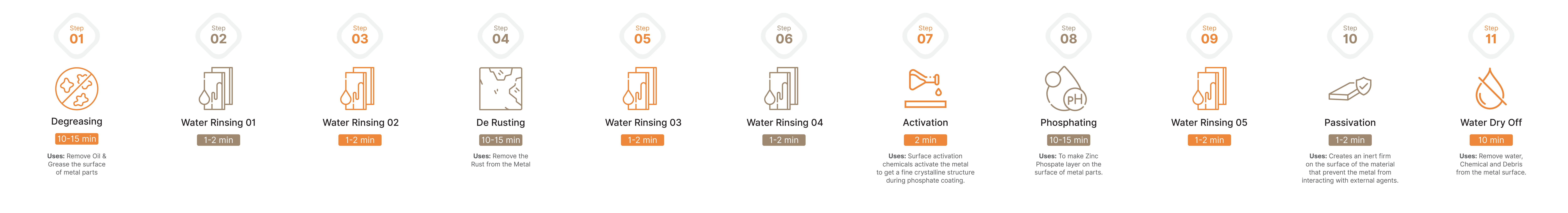

Steel
Pre Treatment
Mild steel pre-treatment is a preparation process for mild steel surfaces before painting, coating, or further fabrication to enhance adhesion, protect against corrosion, and improve the durability of the final product. Because mild steel is prone to rust and corrosion, pre-treatment is crucial in preventing degradation, especially in environments exposed to moisture or chemicals. The outcome of pre-treatment is:
Increased Corrosion protection:
Pre-treatment can create a protective layer that prevents corrosion and extends the life of the metal.
Durability
Pre-treatment can make a coating more resistant to weathering, abrasion, and chemicals.
Minimizing Environmental impact:
Pre-treatment can reduce the need for re coating, which can minimize environmental impact.
Broad applicability:
Chemical pre-treatment methods can be used on all types and sizes of metal workpieces.
Metal Specification
Mild steel, also known as low-carbon steel, is a type of carbon steel with a low carbon content and is primarily made of iron. The composition of mild steel can vary based on the grade and intended use.
- Physical properties: High tensile strength, high impact strength, good ductility and weldability, magnetic metal, good malleability
- Chemical properties: Low carbon content, little sulfur and copper
- Density: 7,860 kg/m³
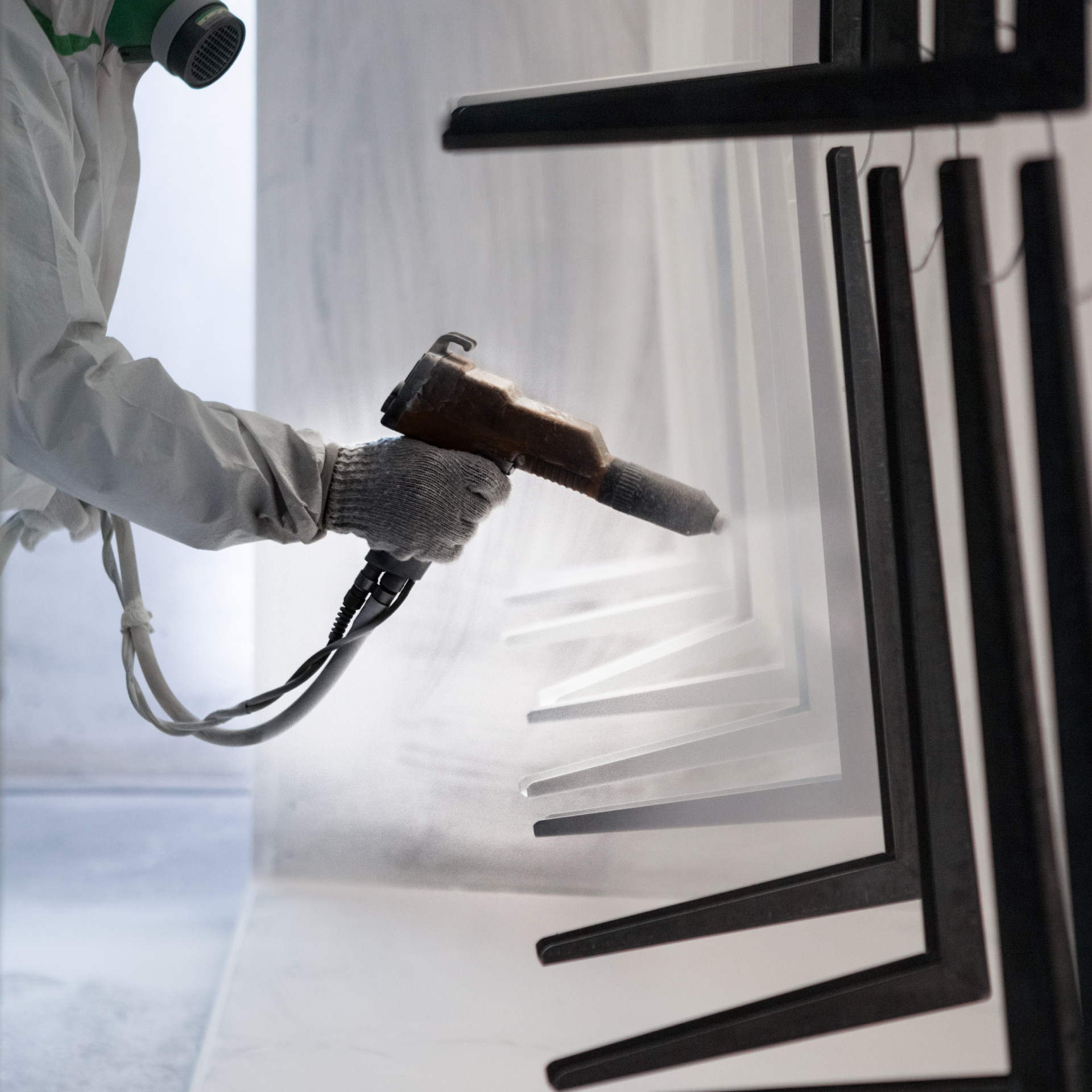


Powder Coating
Powder Coating is a finishing process used on steel, where a dry powder is applied electrostatically and then cured under heat to form a durable, protective layer. This process provides a smooth, even coat that is scratch resistant, corrosion resistant, doesn’t fade for a very long time, and wear resistant.
Unlike traditional liquid paint, powder coating does not require solvents, making it a more environmentally friendly option. Powder coating offers several advantages like, it produces minimal waste, emits little to no volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and has a long-lasting finish.
Disclaimers
Primary material is the main material used to manufacture the product and in addition to the primary material there might also be other type of materials used in the manufacturing of the product
